The Direct Garmin integration in m-Path enables researchers to collect continuous physiological measurements directly from participants’ Garmin smartwatches. Unlike the standard wearable integration, this feature provides direct communication between the m-Path Sense app and Garmin devices, allowing for higher-resolution data collection and trigger-based interventions.
Key Features
- Raw data collection with customizable sampling rates(measure and device dependent).
- Privacy-friendly: Participant data is transferred directly from the watch to the m-Path Sense app, no third-party integrations or apps required.
- Trigger-based interventions: Enables you to create conditions that trigger notifications or questionnaires based on Garmin data.
1. Setting Up Direct Garmin Integration
Create a Garmin sensing setup
To begin collecting data from Garmin devices, create an interaction and add a Sensing setup item from the m-Path dashboard. Then enable the Garmin sensors you want for your study.
The “Garmin High Heart Rate and High Stress Trigger” item is available as an example in the interaction library. For background information on sensing concepts and configuration, see the Mobile Sensing manual.
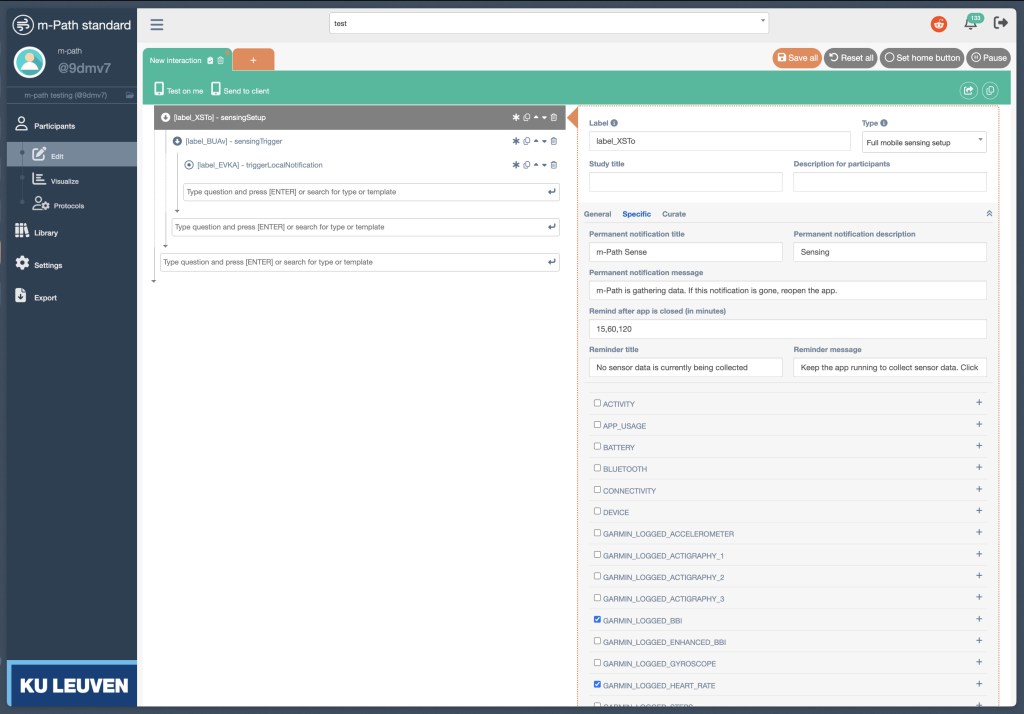
Configure sampling rates
Each Garmin sensor can be configured with a sampling interval (seconds) that determines how often entries are logged on the watch. For example, setting the interval to 1 for heart rate logs a value every second.
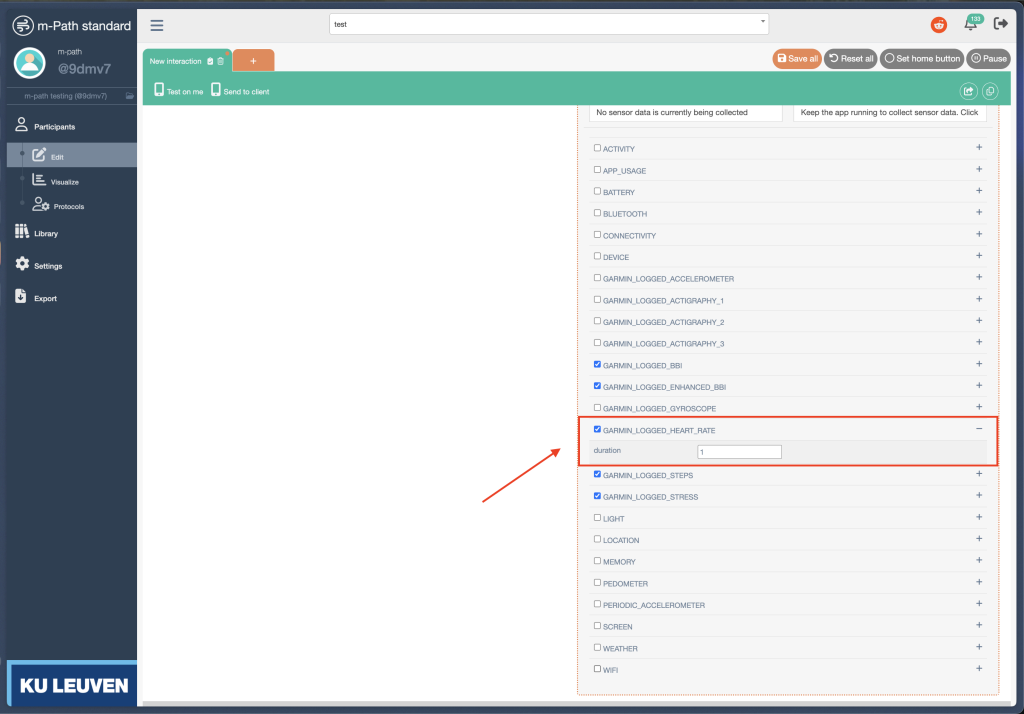
Valid sampling intervals
Not all measures support configurable sampling. The table below lists valid intervals and limitations.
| Measure | Default | Minimum | Maximum | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBI (Beat-to-Beat Interval) | N/A | N/A | N/A | No processing interval required; all IBI values recorded by default. |
| Zero Crossing | 30s | 30s | 3600s | Intervals must be multiples of 30 seconds. |
| Steps | 60s | 60s | 60s | Locked at 1 minute. |
| Stress | 10s | 1s | 3600s | Intervals below 10 seconds may not update between recordings (device dependent). |
| Heart Rate | 30s | 1s | 3600s | |
| SpO2 | 30s | 1s | 3600s | |
| Respiration | 10s | 1s | 3600s | Intervals below 10 seconds may not update between recordings (device dependent). |
| Accelerometer | N/A | N/A | N/A | Raw accelerometer at 25Hz. Not configurable. Very high data rate. Requires frequent sync and can significantly affect battery life. |
| Gyroscope | N/A | N/A | N/A | Raw gyroscope at 32Hz. Not configurable. Very high data rate. Requires frequent sync and can significantly affect battery life. |
Set up Garmin triggers
You can create triggers based on incoming Garmin data. To configure triggers:
- Add a Sensing trigger as an underlying item for the sensing setup. Your setup should look like this:

- Select a Garmin trigger type:

- Define the trigger conditions using computations (see Computation item (pseudo R)).
Available extract labels for Garmin data
When writing trigger computations, you can extract specific data using the extract(newSensorData, 'label') function. Below are all available extract labels organized by measurement type:
Heart Rate
heartRates– Vector of heart rate values (BPM)heartRateTimestamps– Vector of timestamps for heart rate measurementsheartRateStatuses– Vector of status strings (e.g., “locked”, “unlocked”)
Stress
stressValues– Vector of stress scores (0-100)stressTimestamps– Vector of timestamps for stress measurementsstressStatuses– Vector of status strings
Steps
stepValues– Vector of step counts per intervaltotalStepsPerEntry– Vector of cumulative steps since midnightstepsStartTimestamps– Vector of interval start timestampsstepsEndTimestamps– Vector of interval end timestamps
BBI (Beat-to-Beat Interval)
bbiValues– Vector of BBI values in millisecondsbbiTimestamps– Vector of timestamps for BBI measurements
Enhanced BBI
enhancedBbiValues– Vector of enhanced BBI values in millisecondsenhancedBbiGapDurations– Vector of gap durations in millisecondsenhancedBbiTimestamps– Vector of timestampsenhancedBbiStatuses– Vector of status strings
Respiration
respirationRates– Vector of breaths per minuterespirationTimestamps– Vector of timestampsrespirationStatuses– Vector of status strings
SpO2 (Blood Oxygen)
spo2Values– Vector of SpO2 percentage readingsspo2Timestamps– Vector of timestamps
Accelerometer
accelerometerXValues– Vector of X-axis values in milli-gaccelerometerYValues– Vector of Y-axis values in milli-gaccelerometerZValues– Vector of Z-axis values in milli-gaccelerometerTimestamps– Vector of timestamps
Gyroscope
gyroscopeXValues– Vector of X-axis values in degrees/secondgyroscopeYValues– Vector of Y-axis values in degrees/secondgyroscopeZValues– Vector of Z-axis values in degrees/secondgyroscopeTimestamps– Vector of timestamps
Skin Temperature
skinTemperatureValues– Vector of temperature values in °CskinTemperatureTimestamps– Vector of timestampsskinTemperatureStatuses– Vector of status strings
Wrist Status
wristStatuses– Vector of wrist status strings (on-wrist/off-wrist)wristStatusTimestamps– Vector of timestamps
Example: Simple heart rate trigger
Trigger when the average heart rate in the new Garmin data exceeds a threshold:
doTrigger = 0
# Extract heart rate data
heartRates = extract(newSensorData, 'heartRates')
# Handle missing data (e.g., watch off-wrist)
if(is.na(mean(heartRates))){
heartRates = 0
}
# Calculate average and trigger
avgHR = nanmean(heartRates)
if(avgHR > 80){
doTrigger = 1
}Then configure the trigger in the builder:
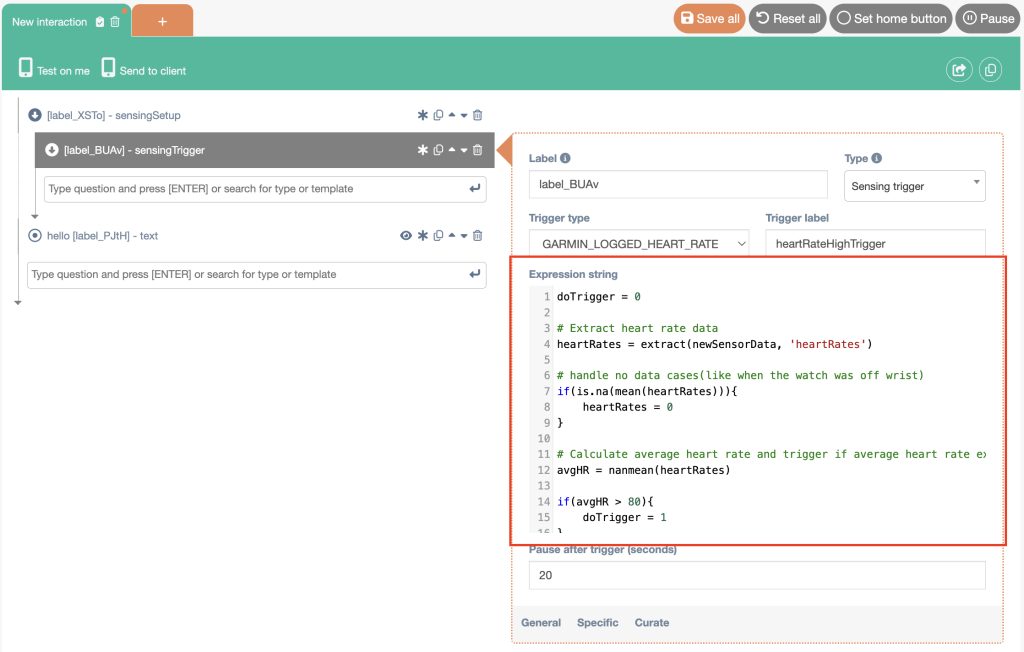
After saving your sensing setup + trigger, it’s ready to send to participants via an interaction (e.g., as part of an intake questionnaire).
Example: Combine multiple Garmin measures in one trigger
You can combine measures (e.g., heart rate + stress) to trigger when multiple conditions are met:
doTrigger = 0
# Extract heart rate
heartRates = extract(newSensorData, 'heartRates')
# Extract stress
stressValues = extract(newSensorData, 'stressValues')
# Handle missing data
if(is.na(mean(heartRates))){
heartRates = 0
}
if(is.na(mean(stressValues))){
stressValues = 0
}
# Check combined conditions
if(length(heartRates) > 0 && length(stressValues) > 0){
avgHR = mean(heartRates)
avgStress = mean(stressValues)
# Trigger if BOTH are high
if(avgHR > 50 && avgStress > 30){
doTrigger = 1
}
}Example: Using entry counts for data quality checks
Check if enough data is available before triggering:
doTrigger = 0
# Get the count of heart rate measurements
hrCount = extract(newSensorData, 'heartRateCount')
# Only proceed if we have sufficient data
if(hrCount > 10){
heartRates = extract(newSensorData, 'heartRates')
avgHR = mean(heartRates)
if(avgHR > 100){
doTrigger = 1
}
}2. Participant Setup and Pairing
Send the sensing setup to participants
Once configured, send the sensing setup item to participants through an interaction (this can be part of an intake questionnaire). When participants encounter the sensing setup item, they are guided to pair their Garmin watch.
Bluetooth pairing process
The pairing process uses BLE to establish a direct connection between the participant’s phone and their Garmin watch.
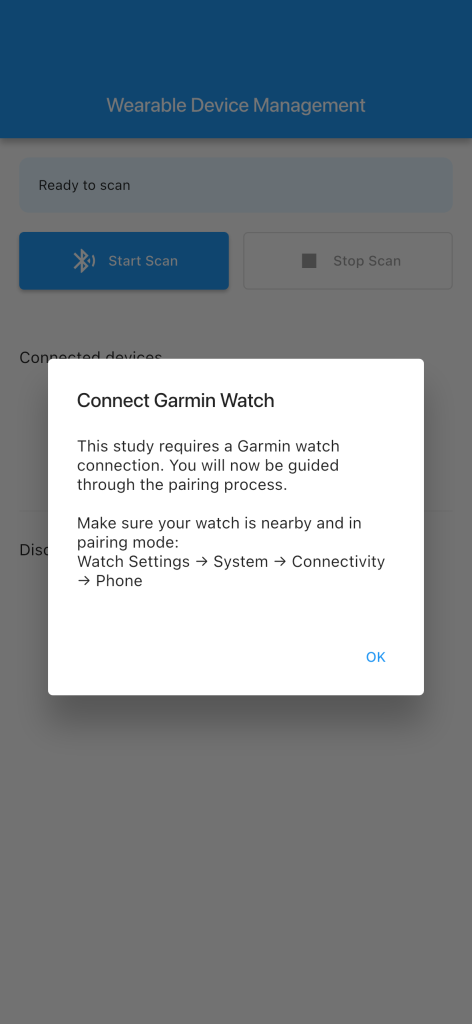
The m-Path Sense app scans for nearby Garmin devices:
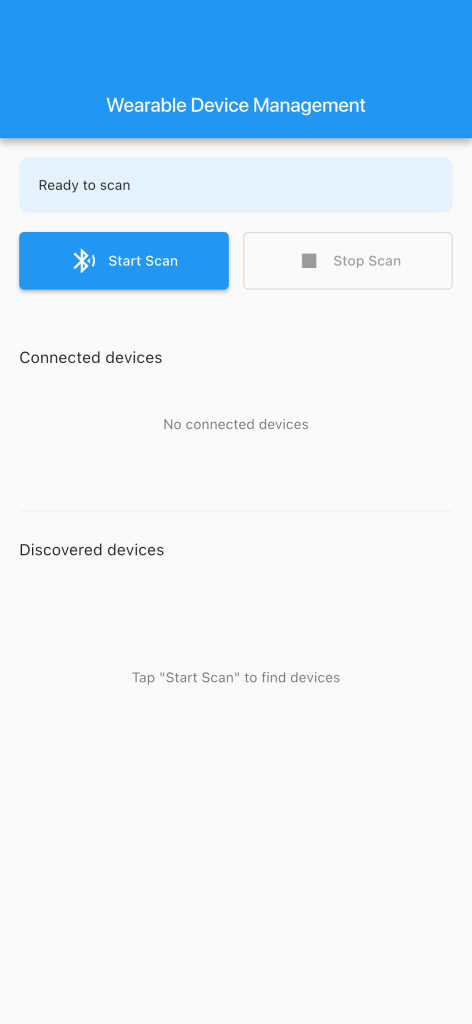
Participants select their watch from the list of available devices and the app establishes a connection with the watch
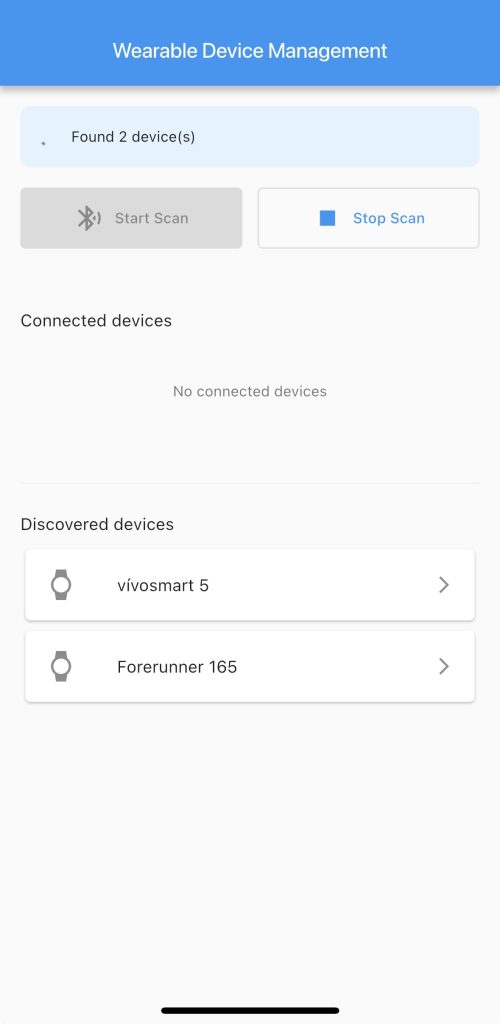
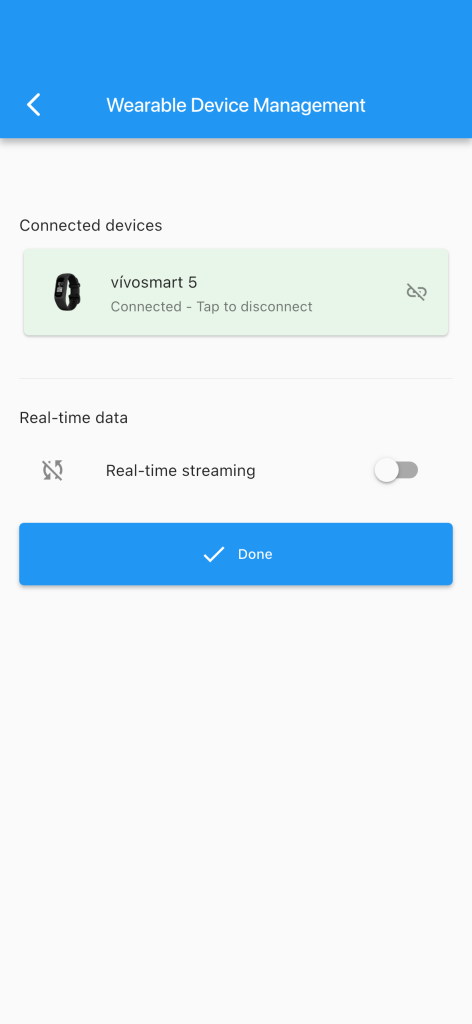
After pairing, participants can continue the interaction.
Pre-pairing checklist
BLE pairing can fail for several reasons. Before attempting to pair, ensure that:
- The Garmin watch is not connected to another phone or device.
- Bluetooth is enabled on the participant’s phone.
- The watch is in pairing mode.
- If pairing fails, consult the pairing issues guide.
3. Data Collection and Monitoring
Background sensing
Once paired successfully, the m-Path Sense app continuously collects data from the Garmin watch in the background. Participants do not need to keep the app open for data collection to occur.
Like other sensors in m-Path Sense, direct Garmin sensing runs continuously until:
- The app is killed by the operating system (iOS or Android).
- The participant manually closes the app.
- Bluetooth connection fails (disabled by the user, watch is dead/out of range)
Data sync and chunking behavior
The m-Path Sense app automatically syncs data from the Garmin watch at regular intervals. When syncing data after a large time gap (for example, when the app has been closed for several hours), the system automatically splits the data into 15-minute chunks to ensure reliable processing and upload.
This means that a single sync session may produce multiple measurement entries in your exported data, each covering a 15-minute window. This chunking behavior is automatic and requires no configuration.
Restart reminders
If the app stops gathering data (for example, if it is killed by the operating system), participants will receive a reminder notification to resume the app. This works the same as other m-Path Sense sensors.
You can configure reminder notifications in the sensing settings.
4. Exporting and Analyzing Data
Data export
Data collected through Direct Garmin integration is exported the same way as other Mobile Sensing data. Data is uploaded from the participant’s phone to a pCloud or OneDrive location configured in the researcher dashboard (see Adding a cloud storage location for client file uploads).
Data structure
Garmin sensing data is exported in JSON format, similar to other m-Path Sense data. Each measurement includes a sensorStartTime and a data object containing metadata (time window, entry counts) and the recorded samples.
{
"sensorStartTime": 1765198435067150,
"data": {
"__type": "dk.cachet.carp.garminalllogsdata",
"fromTime": "2025-12-08T13:51:50.101",
"toTime": "2025-12-08T13:53:50.102091",
"entryCounts": {
"heartRate": 118,
"stress": 2,
"steps": 2,
"bbi": 76,
"enhancedBbi": 150,
"respiration": 2,
"spo2": 2,
"accelerometer": 2150,
"gyroscope": 0,
"wristStatus": 0,
"zeroCrossing": 2,
"skinTemperature": 0,
"actigraphy1": 2,
"actigraphy2": 2,
"actigraphy3": 2
},
"heartRate": [
{
"macAddress": "E6:82:85:38:8C:A9",
"timestamp": 1765198310000,
"beatsPerMinute": 73,
"status": "locked"
}
]
}
}Garmin Measurement Types
AccelerometerData
Captures three-axis acceleration data from the device’s accelerometer.
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)timestamp(Date): Timestamp for the accelerometer samplexValue(Float): X-axis in milli-gyValue(Float): Y-axis in milli-gzValue(Float): Z-axis in milli-g
ActigraphyData
Processed activity metrics derived from accelerometer data over a configured interval.
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)startTimestamp(Date): Start timestamp (seconds precision)endTimestamp(Date): End timestamp (seconds precision)instance(String): Actigraphy instance identifiertotalEnergy(UInt32): Accumulated magnitude of accelerationtimeAboveThreshold(Float): Time (seconds) above the configured thresholdzeroCrossingCount(UInt32): Zero crossings over the interval
BBIData
Beat-to-beat interval (time between consecutive heartbeats).
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)timestamp(Date): Timestampbbi(UInt32): Interval in milliseconds
EnhancedBBIData
Enhanced beat-to-beat interval data with status information and gap detection.
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)timestamp(Date): Timestampbbi(UInt32): Interval (ms) if valid; otherwise 0gapDuration(UInt32): Gap duration (ms) when there is a gap in the heart rate signal; otherwise 0status(String): Status of the entry (e.g., “valid”, “gap”)
GyroscopeData
Captures three-axis rotational data from the gyroscope.
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)timestamp(Date): TimestampxValue(Float): X-axis in degrees/secondyValue(Float): Y-axis in degrees/secondzValue(Float): Z-axis in degrees/second
HeartRateData
Heart rate measurements (beats per minute).
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)timestamp(Date): Timestamp (seconds precision)beatsPerMinute(UInt32): BPM valuestatus(String): Sensor status (e.g., “locked”, “unlocked”)
RespirationData
Breathing rate (breaths per minute).
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)timestamp(Date): Timestamp (seconds precision)breathsPerMinute(Float): BPM value (0.0 if unavailable, check status)status(String): Measurement status
SPO2Data
Blood oxygen saturation (%).
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)timestamp(Date): Timestamp (seconds precision)spo2Reading(UInt32): SpO2 percentage
SkinTemperatureData
Skin temperature (°C).
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)timestamp(Date): Timestamp (seconds precision)temperature(Float): Temperature in °C (0–65°C, 0.0 if unavailable)status(String): Measurement status
StepData
Step counts over time intervals.
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)startTimestamp(Date): Start timestamp (seconds precision)endTimestamp(Date): End timestamp (seconds precision)stepCount(UInt32): Steps in the intervaltotalSteps(UInt32): Steps since midnight up toendTimestamp
StressData
Stress scores derived from HRV and related metrics.
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)timestamp(Date): Timestamp (seconds precision)stressScore(Int32): 0–100 (≤25 indicates resting, 0 if unavailable)status(String): Measurement status
WristStatusData
Indicates whether the watch is currently worn.
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)timestamp(Date): Timestampstatus(String): On-wrist / off-wrist
ZeroCrossingData
Activity metrics based on acceleration patterns and energy expenditure.
macAddress(String): Device MAC address (Android) or UUID (iOS)startTimestamp(Date): Start timestamp (seconds precision)endTimestamp(Date): End timestamp (seconds precision)zeroCrossingCount(UInt32): Count of crossings around the average total accelerationtotalEnergy(UInt32): Energy over the interval (rolling window updates)deadband(UInt32): Threshold (milli-g) required for a zero crossing to count (0 if not set)
Troubleshooting pairing issues
Watch not visible during scanning
- Confirm the watch is not already paired with another device.
- Toggle Bluetooth off and on on the phone.
- If the problem persists, perform a factory reset on the Garmin watch and try again.
Pairing process fails
If pairing fails or gets stuck:
- Restart the app and try connecting from the Wearable device management screen.
- If it still fails:
- Close the m-Path Sense app completely.
- Open the phone’s system Bluetooth settings. If the Garmin device appears as paired, Forget/Remove it.
- Toggle Bluetooth off and on.
- Reopen m-Path Sense and retry pairing from Wearable device management.
Connection lost after initial pairing
If a watch was successfully paired but fails to reconnect on a later app start, m-Path Sense will automatically prompt the participant to pair again and show the connection screen.
